Out of Concept and Use: The Development of Heat Transfer Devices

Heat exchangers are critical components in various industries, playing a crucial role in the exchange of thermal energy between multiple fluids. From warming water in residential buildings to controlling temperatures in power plants, understanding what a heat exchanger is and how it works is essential for engineers and decision-makers alike. As the demand for energy efficiency and sustainability grows to rise, the evolution of heat exchanger technology has turned into increasingly significant, leading to innovative designs and applications that meet current industrial needs.
In this article, we will examine the different types of heat exchangers, analyzing their distinct characteristics and functions. We will delve into the key roles they play in HVAC systems, power plants, and renewable energy systems, highlighting their impact on energy efficiency and running costs. By understanding the newest advancements and maintenance strategies, as well as the importance of choosing the right heat exchanger for specific applications, readers will gain important insights into how these noteworthy devices contribute to our everyday lives and the industries that drive our economy.
Understanding Heat Exchangers
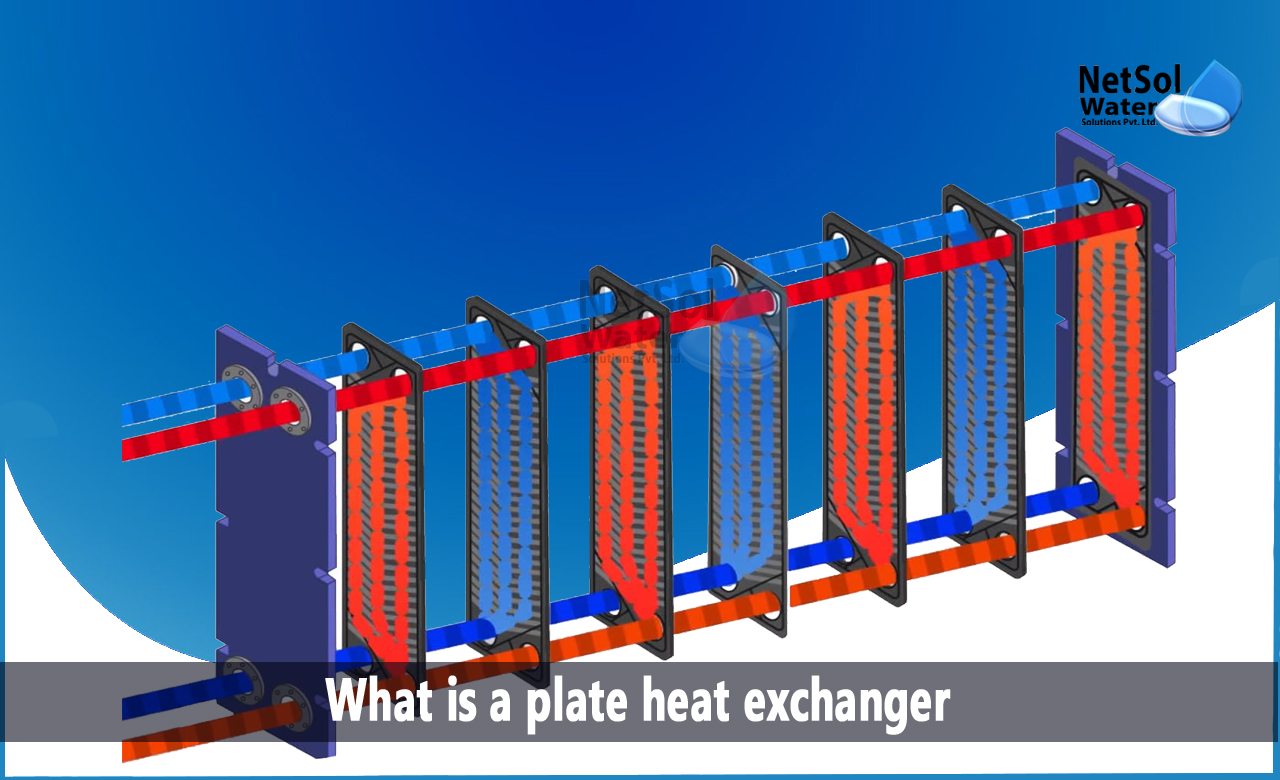
Heat exchangers are crucial components in various industries, enabling the transfer of heat between multiple fluids without them blending. This effective transfer is key for applications ranging from heating and cooling systems to energy production and chemical processing. By applying principles of thermodynamics, heat exchangers manage temperatures and enhance energy efficiency.
The mechanics of a heat exchanger involve the flow of heated and cold fluids through a chain of pipes or plates, keeping a constant temperature difference. This arrangement allows energy to be exchanged from the heated fluid to the cooler one, effectively warming or chilling one of the fluids. The effectiveness of this energy transfer is determined by various factors, including the blueprint of the heat exchanger, the specific heat capacities of the fluids, and the circulation arrangement.
Understanding the different types of heat exchangers is important for selecting the appropriate one for a specific application. From tube and shell to plate-and-fin types, each type offers unique benefits and is fitted for different operational conditions. As fields continue to evolve, advancements in heat exchanger technology aim to enhance efficiency, minimize costs, and improve eco-friendliness in energy utilization.
Uses and Benefits
Heat transfer devices are widely employed across multiple industries, serving as key components in systems that involve the transfer of thermal energy between liquids. In energy facilities, they play a crucial role in temperature regulation, enabling optimal energy conversion and maintaining optimal operational temperatures. Similarly, in the heating, ventilation, and air conditioning sector, heat exchangers boost indoor climate control, facilitating energy efficiency and enhanced comfort in residential and commercial spaces. Their capability to transfer heat effectively makes them essential in refrigeration systems, where they help maintain desired temperatures for food preservation.
Another notable application of heat exchangers is in the chemical industry, where they assist reactions that require precise temperature management. By efficiently transferring heat away from or towards chemical processes, these devices prevent overheating and ensure ideal reaction rates, which is essential for security and productivity. In the food and beverage manufacturing sector, heat exchangers are essential for pasteurization and sterilization, ensuring food safety while preserving quality. Their use not only optimizes production efficiency but also helps businesses meet compliance requirements.
The gains of heat exchangers extend past their functionality in different applications. They contribute to energy efficiency by reducing operational costs and cutting waste. For instance, by recovering waste heat in manufacturing processes, facilities can enhance overall energy utilization and reduce their carbon footprint. Moreover, modern advancements in heat exchanger design, such as compact configurations and advanced materials, are driving sustainability in industries that rely on efficient thermal management systems. This development highlights the integral role of heat exchangers in encouraging environmental responsibility and operational excellence.
Maintenance and Advancements
Proper maintenance of heat exchangers is essential for ensuring their sustained performance and efficiency. Regular inspections help identify problems such as fouling, corrosion, or leaks that can degrade performance and increase energy costs. Establishing a routine maintenance schedule, which consists of cleaning, checking for signs of wear and tear, and assessing thermal performance, can extend the lifespan of heat exchangers significantly. Additionally, employing digital monitoring technologies can provide real-time data on operational conditions, enabling proactive maintenance interventions before larger issues arise.
Advancements in heat exchanger design are driving improvements in efficiency and sustainability. Compact heat exchangers are becoming increasingly popular due to their ability to deliver high thermal performance in a more compact footprint, making them ideal for limited space applications. Improvements in materials, like the use of titanium and high-grade stainless steel, enhance durability and resistance to corrosion, which is critical in harsh operating environments. Moreover, Home page as microchannel heat exchangers and 3D printing of heat exchanger components are paving the way for customized solutions that meet specific industrial challenges.
As industries continue to prioritize energy efficiency and sustainability, the role of heat exchangers is changing. The integration of smart technologies enables better energy management and real-time performance optimization, which is vital in applications ranging from HVAC systems to renewable energy. The development of environmentally friendly refrigerants and the design of heat exchangers that facilitate energy recovery further underline the sector’s commitment to reducing carbon footprints. As these innovations continue to flourish, heat exchangers will remain a key component in driving the future of energy-efficient systems.
